What Must Be Added or Removed to Change the State of Matter?
When cubes of water ice cook into water or liquid boils into vapour, you may take seen changes in states of affair, only take you ever wondered why the substances modify their form? When affair loses or gains energy, it changes its status. When a substance gains energy, its molecules or atoms move faster, and extra kinetic energy pushes the particles at a sufficient altitude apart from one another that their shape changes. Typically, this free energy is called thermal energy or heat. Let us look at the science supporting the shifting states of affair in this post.
Change of state
A physical change in a matter is referred to as a change of condition. They are reversible alterations that exercise not entail any modifications to the matter's chemical limerick. Deposition, melting, sublimation, freezing, vaporisation and condensation are examples of country transitions. The modifications are depicted in the diagram below.
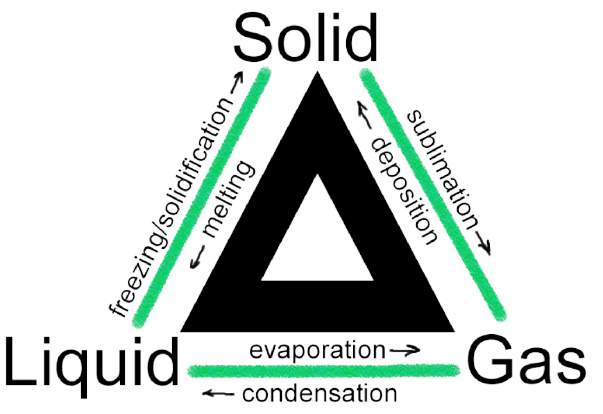
What Causes Phase Changes?
Change of phase occurs when a system's force per unit area or temperature changes. The contact between particles increases as pressure or temperature rises. Similarly, when the temperature falls, atoms and molecules discover it simpler to form a more hard structure.
1. Alter of stage between solids and liquids
In a tray, how would you form ice cubes? To begin, the tray is filled with water from a faucet. The tray would then be placed in the refrigerator's freezer compartment. The freezer is really frigid. And so, what'south adjacent?
- Freezing: Rut is transferred from the warmer tray to the freezer's colder air. The warm water in the freezer loses rut to the chilly air. This oestrus transfer continues until the particles lose all their free energy to move past each other. They are compelled to remain in fixed places considering of the forcefulness of attraction between them. Water (liquid) is transformed into ice (solid) in this manner. Therefore, freezing is the process of the transformation of h2o into solid. The freezing point is the temperature at which the transformation happens.
- Melting: The ice cubes would absorb free energy from the warmer air surrounding them if they were removed from the freezer and placed in a warm area. The absorbed energy would help them to bargain with the force of attraction that bound them together, assuasive them to break gratis from their ice-like grip. Melting is the transformation of a solid into a liquid state. Melting bespeak is the temperature at which a solid transforms into liquid.
two. Change of phase between gases and liquids
The water warms up when you fill a pot with common cold tap water and heat it on a hot cooktop. Heat free energy flows from the cooktop to the pot, where it is absorbed by the water. What will happen to the water afterward that?
- Vaporization: If the water is sufficiently heated, it will begin to boil. In the humid water, water vapor bubbles develop. This occurs when liquid water particles obtain enough energy to overcome the force of attraction betwixt them and transition to a gaseous form. The bubbling rising through the h2o and exit as steam, which escapes from the pot. Vaporization is the process through which a liquid boils and transforms into a gas. The boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which it boils.
- Condensation: The mirror is decumbent to fog up when yous take a hot shower in a closed bath. You might be wondering why this occurs. As hot h2o from the shower evaporates, it cools and loses energy when it comes into impact with colder surfaces, such as the mirror. The energy required by the colder h2o particles to overcome the forces of attraction betwixt them is no longer bachelor. They clump together and create liquid h2o aerosol. Condensation is the process through which gas transforms into a liquid.
3. Change of phase between gases and solids
Solids that transform to gas must first pass through a liquid status. Solids may, on the other mitt, transform from solid to gas without passing through the liquid state. The opposite change can besides happen. Gases tin can sometimes catechumen straight to solids.
- Sublimation: Sublimation is the process of solids converting straight to gases. When solids absorb enough energy, the forces of attraction betwixt them are totally eliminated. Sublimation occurs when solids, such as dry ice, are heated. We tin can't forget near air fresheners while we're talking about sublimation examples. Solid air fresheners (such as those used in toilets) take a distinction for being exquisite in nature.
- Degradation: Deposition is a stage alter in which a gas becomes a solid without start passing through the liquid phase. Thermodynamics governs the procedure of deposition. Sublimation is the inverse of deposition, hence deposition is besides referred to every bit desublimation. For example, h2o vapour in the air transforms to pocket-size ice crystals when warm moist air inside a house comes into touch with a freezing cold windowpane.
Conclusion
- Every item in being experiences a state transition, which you should be enlightened of. It's merely a matter of how much heat is applied to the material.
- Everything on our planet can exist manipulated to change its condition if enough heat is provided. The indicate is, non all substances must take the solid-liquid-gas route.
- Some compounds tin spontaneously transit from a solid to a gaseous state without passing through a liquid phase.
- Sublimation is the term for this process. The dry ice, chemical element iodine, and high-quality coal, which burns and sublimates into vapor at high temperatures, are all examples of sublimation.
- In total, nosotros have witnessed half-dozen changes in states of matter so far.
Sample Problems
Trouble 1: What does information technology take to change the state of matter?
Answer:
It specifies a matter's changing condition when you lot add or remove estrus from it. When you apply heat to a substance, it begins to cook. When the heat is removed, though, it begins to solidify. The motility of particles causes a alter in the state when heat is added or removed from the substance. The atoms in a substance are always moving at various speeds. They gain speed as a outcome of the heat.
Trouble 2: Explain the sentence "The liquid country is a transitional condition between the gaseous and solid states."
Answer:
A liquid has a lower force of attraction than solids just a higher force than a gas. A liquid has more inter-particle gaps than solids and less inter-particle spaces than a gas. This demonstrates that liquids are a transitional state betwixt solids and gases.
Problem three: What are the two types of changes that can happen in a situation?
Reply:
Physical and chemical alterations are the nearly common changes that matter endures. At that place is no change in the identity of a matter after concrete transformation. On the other hand, its shape, size, and status vary. However, if a chemical modify occurs, it cannot exist reversed or is merely reversible under particular conditions.
Problem 4: What is the mechanism through which gases become solids direct?
Respond:
Deposition is the process through which a gaseous land transforms into a solid country without transitioning to a liquid state.
Problem 5: How many unlike states of matter are there?
Answer:
Matter is annihilation in our surround that has its own mass and occupies a sure amount of infinite. It can also be defined equally objects that we can gustation, touch, or smell. For instance, a chair, air, water, aureate, and so on. An cantlet is the smallest particle of matter.
In that location are five forms of affair known to us out of which three are institute nether normal conditions. These are:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
- Plasma
- Bose Einstein
Solid, liquid and gas are common forms out of these matters.
lilienthallogetch39.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/change-of-state-of-matter/
0 Response to "What Must Be Added or Removed to Change the State of Matter?"
Post a Comment